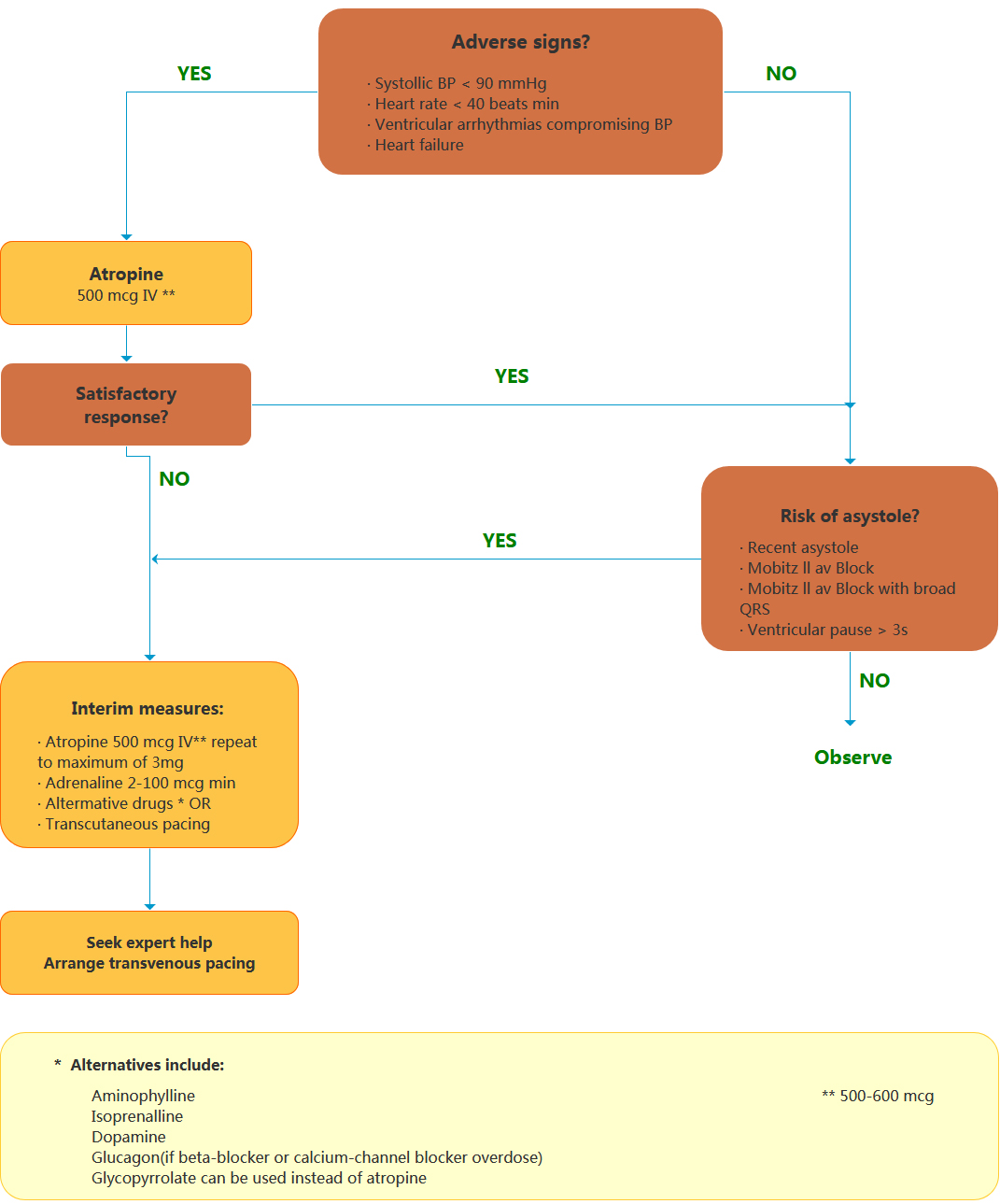
什么是心律失常?
What Is Arrhythmia?
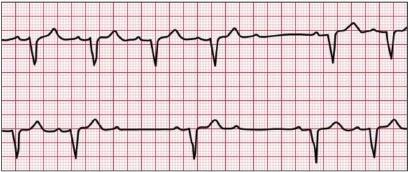
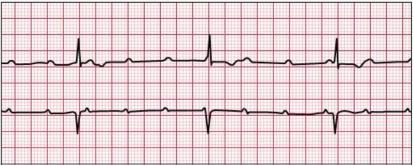
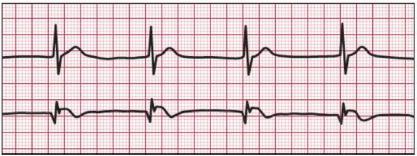
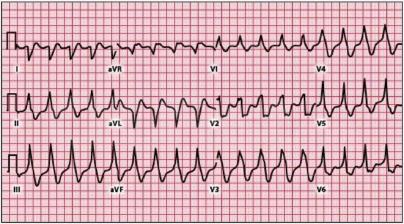
An arrhythmia is an abnormal heart rhythm.It may feel like fluttering or a brief pause.It may be so brief that it doesn’t change your overall heart rate. Or it can cause the heart rate to be too slow or too fast. Some arrhythmias don’t cause any symptoms. Others can make you feel lightheaded or dizzy
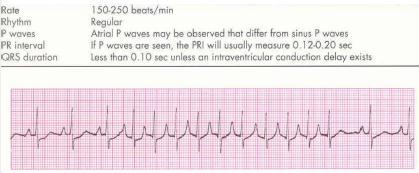
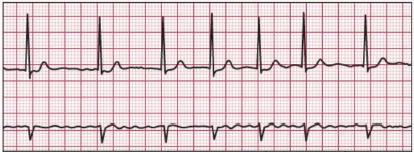
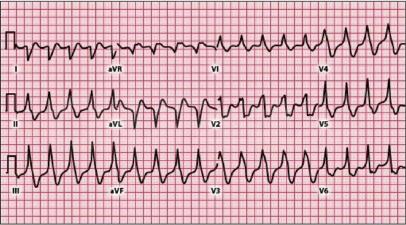
There are two basic kinds of arrhythmias.Bradycardia is when the heart rate is too slow — less than 60 beats per minute.Tachycardia is when the heart rate is too fast — more than 100 beats per minute.
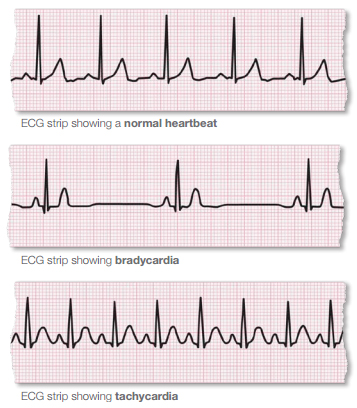
What are the signs of arrhythmia?
- When it’s very brief, an arrhythmia can have almost no symptoms. It can feel like a skipped heartbeat that you barely notice.
- It also may feel like a fluttering in the chest or neck.
- When arrhythmias are severe or last long enough to affect how well the heart works, the heart may not be able to pump enough blood to the body. This can cause you to feel tired, lightheaded or may make you pass out. It can also cause death.
- Tachycardia can reduce the heart’s ability to pump, causing shortness of breath, chest pain,lightheadedness or loss of consciousness. If severe, it can also cause heart attack or death.
What are the signs of arrhythmia?
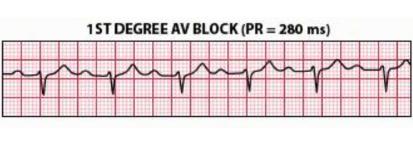
Before treatment, it’s important for your doctor to know where an arrhythmia starts in the heart and whether it’s abnormal. An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is often used to diagnose arrhythmias. It creates a graphic record of the heart’s electrical impulses.Using a Holter monitor, exercise stress tests, tilt table test and electrophysiologic studies (“mapping” the electrical system of your heart) are other ways to find where arrhythmias start. Treatment may include:
- Lifestyle changes
- Medicine to prevent and control arrhythmias
- Medicine to treat related conditions such as high blood pressure, coronary artery disease and heart failure
- Anticoagulants to reduce the risk of blood clots and stroke.
- A pacemaker to help your heart beat more regularly
- Cardiac defibrillation and implanted cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs)
- Cardiac ablation
- Surgery